Vermont Brain Injury Lawyers





Why You Need Vermont Brain Injury Attorneys
If you or a loved one suffered a traumatic brain injury in Vermont, you need experienced legal representation to secure the compensation you deserve.
Brain injuries are often invisible. Unlike a broken bone, others cannot see your pain, memory loss, or emotional struggles. This isolation exacerbates an already difficult situation.
Our personal injury attorneys have helped brain injury victims throughout Vermont recover millions in compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering. At Sabbeth Law, our Vermont brain injury lawyers understand the devastating impact these injuries have on victims and their families, the confusion, the mounting medical bills, and the uncertainty about your future.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
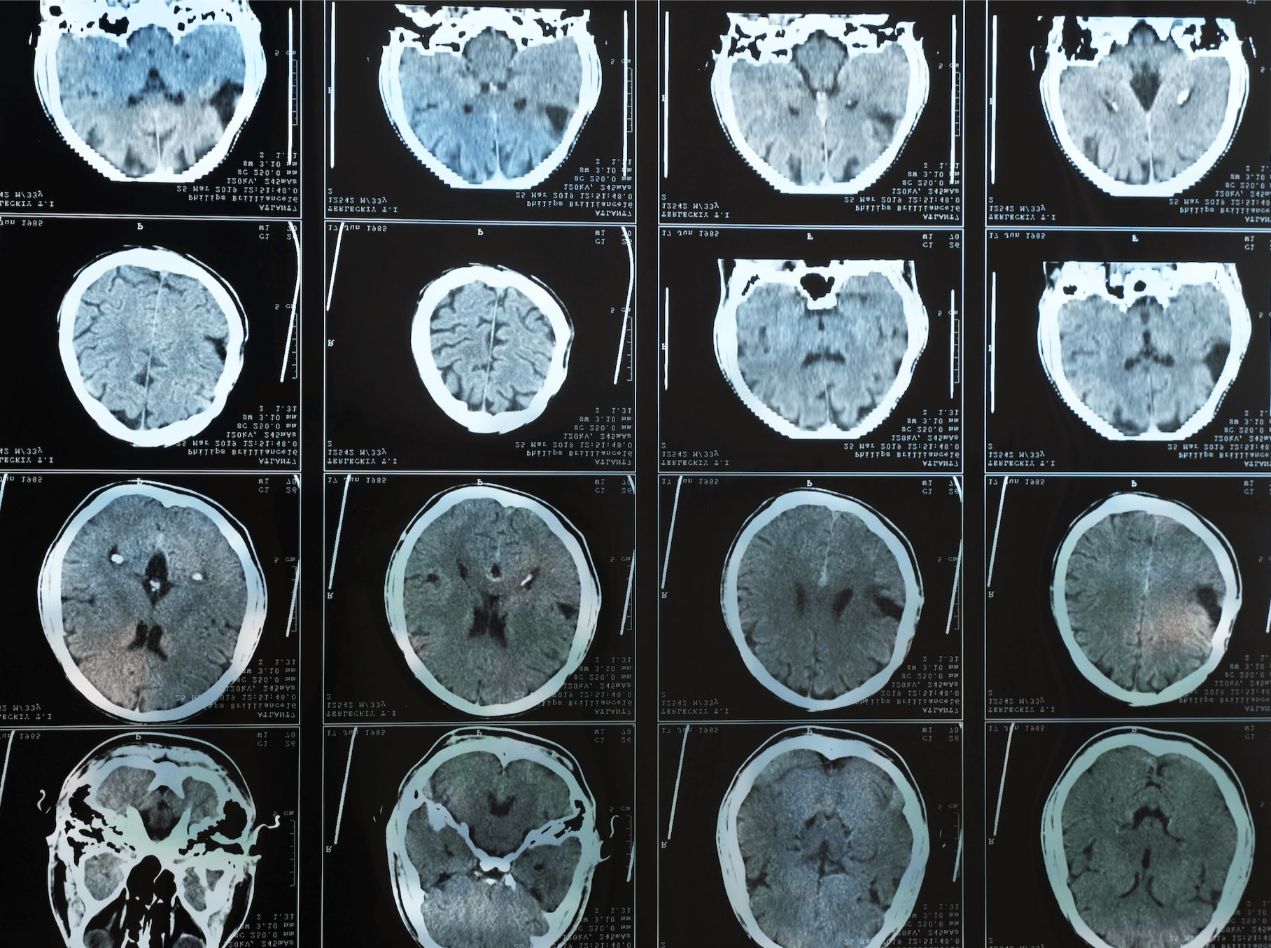
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force damages the brain. This can happen from a sudden blow to the head, a violent jolt to the body, or an object penetrating the skull. Even so-called “mild” brain injuries like concussions can cause lasting complications that affect every aspect of daily life.
Brain injuries fall into two categories. Open brain injuries penetrate the skull, such as from a gunshot or a sharp object. Closed brain injuries, the most common type, occur without skull penetration but can be equally serious. Many closed brain injuries do not appear on imaging tests, leading to delayed diagnoses or misdiagnosis as post-traumatic stress disorder.
Common Brain Injury Symptoms
Brain injury symptoms vary based on severity and the location of damage. Vermont brain injury victims commonly experience:
• Persistent headaches and dizziness
• Memory loss and difficulty concentrating
• Mood swings, irritability, and personality changes
• Sensitivity to light and sound
• Sleep disturbances and chronic fatigue
These symptoms may not appear immediately. Some victims do not notice problems until days or weeks after the accident, which is why seeking medical attention promptly after any head trauma is critical for both your health and your legal claim.
TBI Severity Levels
Mild TBI (Concussion)
Mild TBIs may cause brief or no loss of consciousness. While many concussions heal within weeks to months with rest, some victims experience persistent symptoms that interfere with work and daily activities.
Moderate TBI
Moderate brain injuries typically involve unconsciousness lasting more than 30 minutes and memory loss exceeding 24 hours. Victims often require hospitalization, monitoring, and rehabilitation therapy.
Severe TBI
Severe traumatic brain injuries cause extended unconsciousness and carry high risks of permanent disability or death. Survivors often need years of rehabilitation and ongoing assistance with daily living.
Common Causes and Types of Brain Injuries
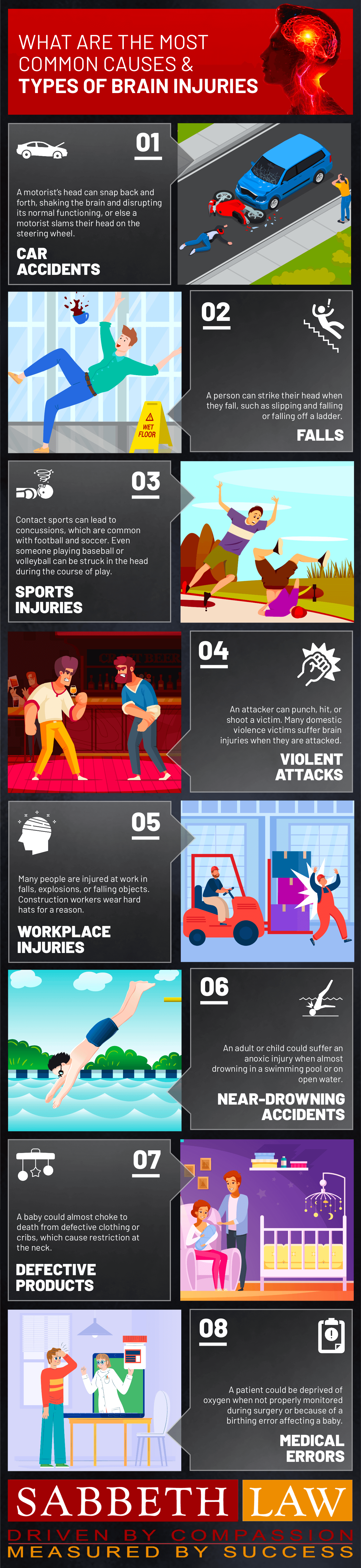
Many brain injuries result from preventable accidents caused by someone else’s negligence. Sabbeth Law handles brain injury cases arising from:
- Car accidents – Head impacts with steering wheels, windows, or violent whiplash motion
- Slip and fall accidents – Falls on icy sidewalks, wet floors, or from heights
- Workplace injuries – Construction site falls, falling objects, and explosions
- Sports injuries – Concussions from contact sports and recreational activities
- Medical malpractice – Surgical errors, anesthesia mistakes, and birth injuries
- Violent assaults – Physical attacks and domestic violence
How Brain Injuries Impact Daily Life
The brain controls everything, including movement, memory, emotions, speech, and reasoning. Any injury can cause dramatic disruptions to work, relationships, and independence.
Brain injury victims commonly struggle with:
- Cognitive difficulties – Problems with concentration, decision-making, and short-term memory that make returning to work impossible
- Emotional changes – Depression, anxiety, mood swings, and personality shifts that strain family relationships
- Physical impairments – Loss of coordination, balance problems, and difficulty with motor skills
- Communication challenges – Speech difficulties and trouble processing conversations
How Sabbeth Law Helps Brain Injury Victims
At Sabbeth Law, we have decades of experience handling complex brain injury claims. We provide comprehensive legal representation, including:
• Thorough investigation of your accident and identification of all liable parties
• Coordination with medical experts and neurologists to document your injuries
• Calculation of current and future damage,s including lifetime care costs
• Aggressive negotiation with insurance companies
• Trial representation when insurers refuse fair settlement offers
Proving Negligence in a Vermont Brain Injury Case
To recover compensation, you must prove four elements: duty of care (the defendant owed you an obligation to act safely), breach (they failed that duty through careless or reckless conduct), causation (their breach directly caused your brain injury), and damages (you suffered measurable financial and non-financial losses).
Evidence in brain injury cases may include accident reports, witness statements, medical records, expert testimony from neurologists, and documentation of how the injury has affected your ability to work and live independently.
Compensation for Brain Injury Victims
Brain injury victims in Vermont may recover compensation for:
- Emergency room treatment, surgeries, and hospitalization
- Ongoing medical care, rehabilitation, and therapy
- Lost wages and diminished earning capacity
- In-home care and assistance with daily living
- Pain and suffering
- Emotional distress, depression, and loss of enjoyment of life
The value of your claim depends on injury severity, treatment costs, and how the injury has affected your ability to work and live independently. Severe brain injuries requiring lifetime care can result in significant settlements or verdicts.
Vermont Statute of Limitations
Under Vermont law, you have three years from the date of injury to file a brain injury lawsuit. While three years may seem like an adequate amount of time, building a strong case requires extensive investigation and expert consultation. Missing the deadline means losing your right to sue. Contact our attorneys promptly to protect your claim.
Contact Our Vermont Brain Injury Lawyers Today
A brain injury can change everything in an instant. You should not have to face mounting medical bills and lost income while struggling to recover. If someone else’s negligence caused your injury, you deserve compensation.
Contact us online for a free consultation. Our Vermont brain injury lawyers work on a contingency basis; you pay nothing unless we recover compensation for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much is my brain injury case worth?
Compensation depends on the severity of the injury, medical costs, lost income, and the impact on your quality of life. Mild concussions may result in claims worth thousands of dollars, while severe TBIs requiring lifetime care can result in settlements or verdicts worth millions.
What if my symptoms appeared days after the accident?
Delayed symptoms are common with brain injuries. Seek medical attention immediately when symptoms appear and inform your doctor about the accident. Medical documentation linking your symptoms to the incident strengthens your claim.
Can I afford a brain injury lawyer?
Sabbeth Law handles brain injury cases on a contingency basis. You pay no upfront fees and owe nothing unless we recover compensation on your behalf. Our free consultation costs you nothing.
What is the most common long-term effect of brain injury?
According to CDC data, 57% of moderate to severe brain injury victims experience physical disability five years after injury, and 55% struggle with unemployment. Cognitive difficulties and emotional changes often persist indefinitely.
How long do I have to file a lawsuit in the state of Vermont?
Vermont’s statute of limitations gives you three years from the injury date. However, building a strong brain injury case takes time. Contact an attorney as soon as possible to preserve evidence and protect your rights.
Practice Areas
Client Testimonials
LUKE PARMENTER“Immediately after my son’s injury at work, he was treated poorly. Over the course of the next few days it became even worse, so I called Mike and he and Crystal have been absolute lifesavers during the process. Mike is not your typical stuffed suit lawyer who only cares about the bottom line he genuinely cares about his clients and his assistant Crystal is beyond amazing! My thanks to you both!”
Client Testimonials
“Immediately after my son’s injury at work, he was treated poorly. Over the course of the next few days it became even worse, so I called Mike and he and Crystal have been absolute lifesavers during the process. Mike is not your typical stuffed suit lawyer who only cares about the bottom line he genuinely cares about his clients and his assistant Crystal is beyond amazing! My thanks to you both!”
LUKE PARMENTER
“I could never ask for a better attorney, to fight for me, to believe in me, and have faith in me, than what I found in Mike Sabbeth, He doesn’t treat you like a client, he treats you as if you are one of his own family members, He will fight for you, with all he has, and is ALWAYS up front and honest with you about everything!”
SANDRA DRUGE
